
By hostmyai September 29, 2025
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is rapidly becoming the foundation of modern business operations, powering everything from customer service chatbots to advanced data analytics and predictive modeling.
As businesses scale, AI applications often need to support multiple users simultaneously—research teams, customer-facing platforms, SaaS solutions, or collaborative AI tools. This demand calls for cloud hosting solutions that are secure, scalable, and optimized for multi-user environments.
Cloud hosting for multi-user AI applications offers a flexible, cost-effective infrastructure that allows organizations to develop, deploy, and manage AI workloads without the heavy investment of on-premises hardware.
The cloud provides elasticity, meaning resources can be scaled up or down based on demand. It also supports distributed teams, enabling multiple users across geographies to work on shared AI platforms in real time.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the fundamentals of cloud hosting for AI, the benefits and challenges of multi-user environments, the critical factors to consider when choosing a provider, and best practices for secure and efficient operations.
Whether you are a startup, a research institution, or a large enterprise, understanding how to optimize cloud hosting for AI will help you leverage its full potential.
Understanding Multi-User AI Applications
Multi-user AI applications refer to platforms, tools, or services where more than one individual interacts with the same AI environment simultaneously.
Examples include collaborative machine learning platforms, AI-driven SaaS products, virtual assistants deployed across departments, or AI-powered analytics dashboards accessible to multiple stakeholders.
Unlike single-user AI setups, multi-user systems introduce additional complexity. They must manage concurrent workloads, maintain data integrity, and provide access controls to prevent unauthorized use.
For instance, in a university research lab, dozens of students and faculty may train machine learning models on the same cloud cluster. Similarly, an enterprise might deploy a natural language processing (NLP) engine that serves multiple departments simultaneously.
The demand for multi-user AI applications is growing because organizations increasingly recognize the value of collaborative intelligence.
Developers want to co-build machine learning models, analysts want real-time insights, and executives need decision-support tools. All of these require platforms that can handle concurrency, scalability, and real-time responsiveness.
Cloud hosting plays a vital role here. Traditional infrastructure often struggles with resource allocation when multiple users interact with the same AI workloads.
With cloud hosting, resources such as CPUs, GPUs, storage, and networking can be dynamically provisioned, ensuring smooth operation even under high loads.
Moreover, advanced cloud platforms provide features like role-based access control, API rate limiting, and workload isolation—making multi-user AI environments secure and reliable.
Benefits of Cloud Hosting for Multi-User AI Applications
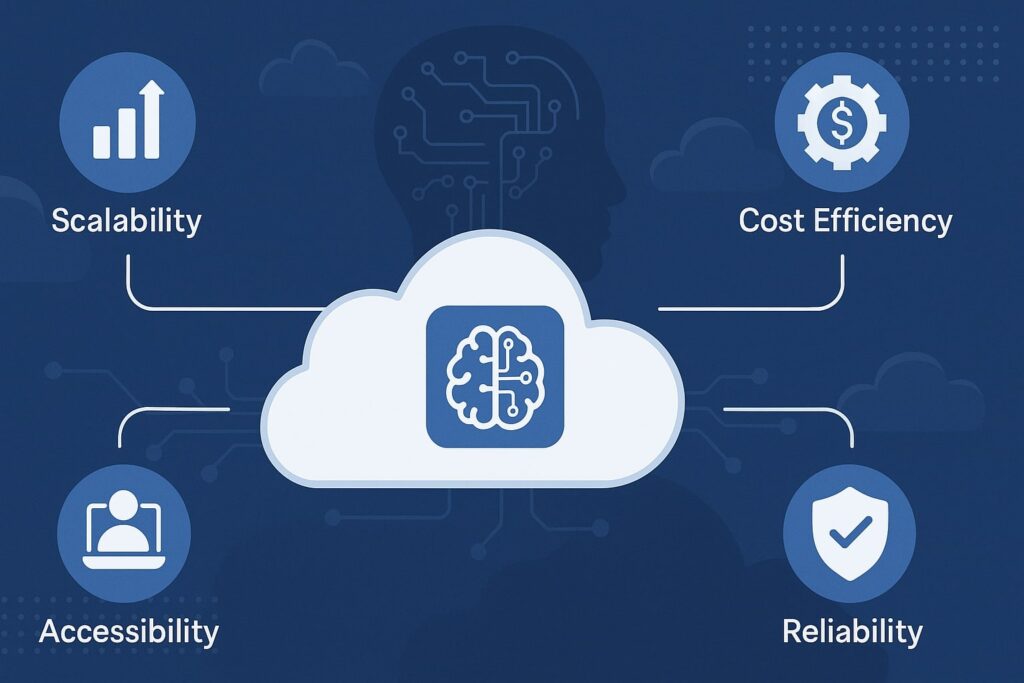
Hosting AI applications in the cloud, particularly those designed for multiple users, provides numerous advantages over traditional hosting. These benefits include flexibility, scalability, cost optimization, and enhanced collaboration.
1. Scalability and Elasticity
One of the key advantages is the ability to scale resources up or down instantly. AI workloads are computationally intensive, especially when dealing with deep learning models or large datasets.
A cloud platform can allocate additional GPUs when usage spikes and scale back during idle times, ensuring cost efficiency. This elasticity is crucial for multi-user environments where demand can be unpredictable.
2. Cost Efficiency
Traditional on-premises infrastructure requires upfront capital investment in servers, networking, and storage. With cloud hosting, businesses shift to an operational expenditure model, paying only for what they use.
Multi-user applications particularly benefit from this pay-as-you-go model since workloads are distributed among many users, and idle resources can be avoided.
3. Collaboration Across Geographies
Cloud hosting allows global access to AI platforms. Teams spread across continents can train models, share datasets, and collaborate in real time. This makes cloud hosting invaluable for research institutions, global enterprises, and SaaS platforms that cater to international users.
4. Security and Compliance
Leading cloud providers invest heavily in security infrastructure, including encryption, firewalls, and compliance certifications (GDPR, HIPAA, SOC 2). Multi-user systems need strong user authentication, data isolation, and logging—capabilities that cloud providers deliver through built-in services.
5. Integration with Advanced Tools
Most cloud platforms offer pre-configured AI and ML services, such as Amazon SageMaker, Google Vertex AI, and Microsoft Azure ML. These integrate seamlessly into hosted environments, allowing developers to quickly deploy AI models with multi-user support.
6. Reduced Management Overhead
Cloud providers handle the underlying hardware, patching, and maintenance, freeing organizations to focus on developing and deploying AI solutions rather than managing infrastructure.
In short, cloud hosting unlocks agility and efficiency for multi-user AI applications, making it the preferred choice for modern organizations.
Challenges in Hosting Multi-User AI Applications in the Cloud
While the cloud offers immense benefits, hosting multi-user AI applications introduces unique challenges that must be addressed for smooth operations.
1. Resource Contention
When multiple users access the same AI application simultaneously, resource contention may occur. GPU and CPU bottlenecks can lead to slow training times or application lag. Without proper workload management, user experience suffers.
2. Cost Overruns
Although the cloud is cost-efficient, multi-user workloads can escalate expenses if resources are not monitored. Idle GPUs, unoptimized training jobs, or unrestricted usage can lead to unexpectedly high bills.
3. Security Risks
Multi-user environments require strict access controls. A single misconfiguration may allow unauthorized access to sensitive data or AI models. Data privacy laws like GDPR make this an even greater concern.
4. Performance Consistency
Cloud environments are shared by multiple tenants. This sometimes leads to “noisy neighbor” effects, where one user’s workload impacts another’s performance. Ensuring consistent performance across users requires careful architecture planning.
5. Complexity of Setup
Deploying AI applications with multi-user support involves configuring identity management, storage systems, networking, and workload orchestration. Organizations without in-house expertise may struggle to design and maintain such environments.
6. Vendor Lock-In
Cloud providers offer proprietary AI services that may not easily migrate to other platforms. Organizations risk dependency on a single provider, limiting flexibility.
By acknowledging these challenges and planning solutions, organizations can maximize the benefits of cloud hosting while mitigating risks.
Key Considerations When Choosing a Cloud Hosting Provider
Choosing the right cloud hosting provider is crucial for ensuring seamless operations of multi-user AI applications. Beyond just cost, several factors influence the effectiveness and efficiency of the hosted environment.
1. GPU and Hardware Options
AI workloads often require high-performance GPUs such as NVIDIA A100 or H100. Ensure the provider offers the necessary hardware at scale. Some providers specialize in AI-optimized infrastructure, which can improve performance and reduce costs.
2. Pricing Structure
Evaluate on-demand, reserved, and spot pricing options. Multi-user workloads may benefit from hybrid pricing strategies to balance cost and performance.
3. Networking and Latency
Applications accessed by users across geographies need low-latency connections. Look for providers with global data centers and robust networking capabilities.
4. Security and Compliance Features
Check whether the provider complies with industry standards such as SOC 2, HIPAA, and GDPR. Features like role-based access control (RBAC), encryption at rest, and audit logs are essential for multi-user systems.
5. AI and ML Ecosystem Support
Providers offering integrated AI services (TensorFlow, PyTorch, Scikit-learn, etc.) reduce the time needed for setup. Prebuilt services can accelerate deployment of multi-user applications.
6. Scalability and Automation
Ensure the provider offers autoscaling capabilities. Multi-user workloads fluctuate, and automation ensures resources adjust dynamically without manual intervention.
7. Support and SLAs
Evaluate the provider’s technical support, uptime guarantees, and service-level agreements (SLAs). For mission-critical AI applications, 24/7 support is essential.
By thoroughly assessing these factors, businesses can select a provider aligned with their specific multi-user AI needs.
Best Practices for Deploying Multi-User AI Applications in the Cloud
Deploying and managing multi-user AI applications requires careful planning to ensure efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and security. Below are some best practices:
- Use Resource Quotas: Set quotas for GPU and CPU usage per user to avoid contention and ensure fair distribution.
- Implement Role-Based Access Control: Restrict access based on user roles. Developers, analysts, and administrators should have different permissions.
- Monitor and Optimize Costs: Leverage cloud-native cost monitoring tools to track spending. Regular audits can prevent overspending.
- Automate Scaling and Orchestration: Use Kubernetes or other orchestration platforms to manage workloads efficiently. Autoscaling ensures performance without wasted resources.
- Prioritize Security: Adopt multi-factor authentication (MFA), encryption, and secure APIs. Regular security audits reduce vulnerabilities.
- Optimize Data Management: AI applications often process large datasets. Use cloud storage solutions with lifecycle management to balance performance and cost.
- Train Teams: Ensure users are trained in best practices for cloud AI platforms. Educated teams reduce risks and improve efficiency.
By following these practices, organizations can deliver a smooth multi-user AI experience while keeping costs and risks under control.
Future of Cloud Hosting for Multi-User AI Applications
The future of cloud hosting for multi-user AI applications is evolving rapidly as advancements in hardware, networking, and AI algorithms accelerate. Emerging trends include:
- AI-Specific Cloud Providers: Companies like CoreWeave and Lambda Labs are offering specialized GPU cloud hosting optimized for AI workloads.
- Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Strategies: Organizations increasingly deploy workloads across multiple providers to avoid vendor lock-in and improve resilience.
- Edge AI Hosting: Multi-user AI applications, particularly those requiring low latency (e.g., autonomous vehicles, IoT devices), will leverage edge computing.
- Serverless AI: The rise of serverless architectures will allow AI applications to scale instantly without pre-allocated infrastructure.
- Improved Collaboration Tools: Cloud providers will offer more built-in features for team collaboration, making it easier for multiple users to co-develop AI models.
As these trends mature, cloud hosting will become even more integral to enabling AI adoption across industries.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q.1: Why should I choose cloud hosting over on-premises for multi-user AI applications?
Answer: Cloud hosting is superior for multi-user AI applications because it eliminates the upfront capital costs of purchasing and maintaining expensive infrastructure.
AI workloads often require high-performance GPUs and large storage systems, which are costly to acquire and maintain on-premises. With cloud hosting, organizations only pay for the resources they consume, making it cost-effective and flexible.
Additionally, cloud platforms provide elasticity, meaning resources can be scaled up or down based on user demand. This is particularly important for multi-user environments, where workloads can fluctuate dramatically.
Cloud hosting also enables collaboration across geographies, providing access to AI environments for distributed teams. For organizations that want agility, scalability, and global accessibility, cloud hosting is the optimal choice.
Q.2: How do cloud providers ensure security in multi-user AI environments?
Answer: Security is a top concern for cloud providers, especially in multi-user setups. Leading platforms implement multi-layered security measures, including encryption at rest and in transit, firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and identity management tools.
They also comply with global standards like SOC 2, HIPAA, and GDPR, ensuring data protection for sensitive workloads.
For multi-user environments, providers offer advanced features such as role-based access control (RBAC), audit logging, and fine-grained permissions. These prevent unauthorized access and ensure that each user can only interact with resources relevant to their role.
Organizations can also integrate multi-factor authentication and virtual private clouds (VPCs) for added protection. Ultimately, the combination of provider security measures and organizational best practices ensures safe multi-user AI operations.
Q.3: What are the main cost challenges of hosting multi-user AI applications in the cloud?
Answer: While cloud hosting is cost-efficient, it can also lead to overruns if not carefully managed. The biggest challenge is unmonitored resource usage.
For instance, if users run GPU instances without shutting them down after completing tasks, costs can escalate quickly. Additionally, multi-user environments often involve simultaneous workloads, which can multiply expenses.
To mitigate these risks, organizations should implement cost monitoring tools, set usage quotas, and adopt policies for shutting down idle resources. Leveraging spot instances or reserved pricing can further reduce costs.
A well-structured governance model ensures that multiple users can operate within budget while still accessing the resources they need.
Q.4: Can I run multi-user AI applications on a hybrid or multi-cloud setup?
Answer: Yes, many organizations deploy multi-user AI applications in hybrid or multi-cloud environments. A hybrid approach allows businesses to combine on-premises infrastructure with cloud resources, providing flexibility for workloads that require local processing alongside scalable cloud capabilities.
Multi-cloud strategies, on the other hand, distribute workloads across multiple providers to reduce dependency on a single vendor.
Running multi-user AI applications on such setups offers resilience, cost optimization, and performance advantages. However, managing hybrid or multi-cloud environments requires strong orchestration tools, standardized data pipelines, and skilled personnel.
Kubernetes and containerization often play a key role in ensuring consistent deployment across multiple environments.
Q.5: What future trends will shape cloud hosting for multi-user AI applications?
Answer: Several emerging trends are expected to shape the future of cloud hosting. First, specialized AI cloud providers offering GPU-optimized infrastructure are gaining popularity, especially for training deep learning models.
Second, serverless AI hosting will grow, allowing instant scaling without pre-provisioned servers. Third, edge AI hosting will expand, supporting multi-user applications requiring real-time decision-making, such as autonomous vehicles or industrial IoT.
Another key trend is improved collaboration features. Cloud providers are introducing built-in tools that allow multiple users to co-develop, annotate, and deploy models simultaneously.
Finally, the push toward multi-cloud and hybrid cloud strategies will continue, helping organizations avoid vendor lock-in while improving reliability. Together, these innovations will make cloud hosting even more central to the future of AI adoption.
Conclusion
Cloud hosting has become the backbone of multi-user AI applications, providing the scalability, flexibility, and global accessibility that modern organizations require. While challenges such as resource contention, cost management, and security must be addressed, the advantages of cloud-based hosting far outweigh the drawbacks.
By carefully selecting providers, adopting best practices, and planning for future trends, businesses can unlock the full potential of AI in collaborative, multi-user environments.
As AI adoption accelerates across industries, cloud hosting will remain essential for ensuring that teams, organizations, and platforms can innovate efficiently and securely. For businesses seeking to empower multiple users with powerful AI capabilities, cloud hosting is not just an option—it is the future.